army judge
Super Moderator
- Jurisdiction
- Other
The World Health Organization (WHO) convened an urgent meeting Tuesday amid an outbreak in Africa of one of the deadliest diseases known to man.
......
Marburg virus disease (MVD) is a rare but severe hemorrhagic fever which affects both people and non-human primates. MVD is caused by the Marburg virus, a genetically unique zoonotic (or, animal-borne) RNA virus of the filovirus family. The six species of Ebola virus are the only other known members of the filovirus family.
Marburg virus was first recognized in 1967, when outbreaks of hemorrhagic fever occurred simultaneously in laboratories in Marburg and Frankfurt, Germany and in Belgrade, Yugoslavia (now Serbia). Thirty-one people became ill, initially laboratory workers followed by several medical personnel and family members who had cared for them. Seven deaths were reported. The first people infected had been exposed to Ugandan imported African green monkeys or their tissues while conducting research. One additional case was diagnosed retrospectively.
The reservoir host of Marburg virus is the African fruit bat, Rousettus aegyptiacus. Fruit bats infected with Marburg virus do not show obvious signs of illness. Primates (including people) can become infected with Marburg virus, and may develop serious disease with high mortality. Further study is needed to determine if other species may also host the virus.
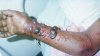
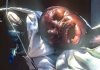
After an incubation period of 2-21 days, symptom onset is sudden and marked by fever, chills, headache, and myalgia. Around the fifth day after the onset of symptoms, a maculopapular rash, most prominent on the trunk (chest, back, stomach), may occur. Nausea, vomiting, chest pain, a sore throat, abdominal pain, and diarrhea may appear. Symptoms become increasingly severe and can include jaundice, inflammation of the pancreas, severe weight loss, delirium, shock, liver failure, massive hemorrhaging, and multi-organ dysfunction.
Clinical diagnosis of Marburg virus disease (MVD) can be difficult. Many of the signs and symptoms of MVD are similar to other infectious diseases (such as malaria or typhoid fever) or viral hemorrhagic fevers that may be endemic in the area (such as Lassa fever or Ebola). This is especially true if only a single case is involved.
The case-fatality rate for MVD is between 23-90%.
......
Marburg (Marburg Virus Disease) | Marburg (Marburg Virus Disease) | CDC
...
The leading health body brought experts from around the world together to discuss how to ramp up the development of vaccines and therapeutics for Marburg virus.
There are growing fears that the world could be caught off guard by the currently untreatable infection that kills up to 88 percent of the people it infects.
WHO convenes 'urgent' meeting over outbreak of deadly Marburg virus | Daily Mail Online
...
https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/marburg/pdf/factsheet.pdf
WARNING, its on the way.
Be very wary...

......
Marburg virus disease (MVD) is a rare but severe hemorrhagic fever which affects both people and non-human primates. MVD is caused by the Marburg virus, a genetically unique zoonotic (or, animal-borne) RNA virus of the filovirus family. The six species of Ebola virus are the only other known members of the filovirus family.
Marburg virus was first recognized in 1967, when outbreaks of hemorrhagic fever occurred simultaneously in laboratories in Marburg and Frankfurt, Germany and in Belgrade, Yugoslavia (now Serbia). Thirty-one people became ill, initially laboratory workers followed by several medical personnel and family members who had cared for them. Seven deaths were reported. The first people infected had been exposed to Ugandan imported African green monkeys or their tissues while conducting research. One additional case was diagnosed retrospectively.
The reservoir host of Marburg virus is the African fruit bat, Rousettus aegyptiacus. Fruit bats infected with Marburg virus do not show obvious signs of illness. Primates (including people) can become infected with Marburg virus, and may develop serious disease with high mortality. Further study is needed to determine if other species may also host the virus.
After an incubation period of 2-21 days, symptom onset is sudden and marked by fever, chills, headache, and myalgia. Around the fifth day after the onset of symptoms, a maculopapular rash, most prominent on the trunk (chest, back, stomach), may occur. Nausea, vomiting, chest pain, a sore throat, abdominal pain, and diarrhea may appear. Symptoms become increasingly severe and can include jaundice, inflammation of the pancreas, severe weight loss, delirium, shock, liver failure, massive hemorrhaging, and multi-organ dysfunction.
Clinical diagnosis of Marburg virus disease (MVD) can be difficult. Many of the signs and symptoms of MVD are similar to other infectious diseases (such as malaria or typhoid fever) or viral hemorrhagic fevers that may be endemic in the area (such as Lassa fever or Ebola). This is especially true if only a single case is involved.
The case-fatality rate for MVD is between 23-90%.
......
Marburg (Marburg Virus Disease) | Marburg (Marburg Virus Disease) | CDC
...
The leading health body brought experts from around the world together to discuss how to ramp up the development of vaccines and therapeutics for Marburg virus.
There are growing fears that the world could be caught off guard by the currently untreatable infection that kills up to 88 percent of the people it infects.
WHO convenes 'urgent' meeting over outbreak of deadly Marburg virus | Daily Mail Online
...
https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/marburg/pdf/factsheet.pdf
WARNING, its on the way.
Be very wary...



